Imagine your workplace ten years from now. Chances are it’ll be very different from today thanks to fast-evolving technologies that are changing the nature of work, the dynamics of the workforce, and the notion of the workplace.
To stay relevant and competitive, you need to understand the impact of emerging technologies on the future of work. You must incorporate these innovations strategically to attract the right talent, increase efficiencies, and improve the bottom line.
How the Future Of Work Will Change
Emerging technologies will impact the future of work in these major categories:
The Nature Of Work
Technologies will minimize the need to perform repetitive tasks manually. While fewer workers will be hired for manual tasks, more will be employed for job functions that involve creative and strategic thinking.
The nature of work will shift from focusing on task completion. Problem-solving, communication, listening, interpretation, and design will gain prominence. The ability to learn new skills will be more valuable than having specific knowledge. Organizations will seek out workers that have the mental ductility to learn continuously. Employees will need to adapt to the “lifelong retooling” of their skillsets.
How Work Is Done
Advances in AI-driven technologies and robotics will increase the range and amount of work that can be done by smart machines. 38% of U.S. jobs (PDF) will likely be automated within the next 15 years, affecting at least 100 million knowledge workers by 2025.
Meanwhile, jobs will become less routine, and roles will be redefined by marrying technology with human skills and advanced expertise. Organizations will need to innovate how humans work alongside machines. They’ll need to rethink how they invest in workers to maximize the impact of human-machine interactions.
Who Does the Work
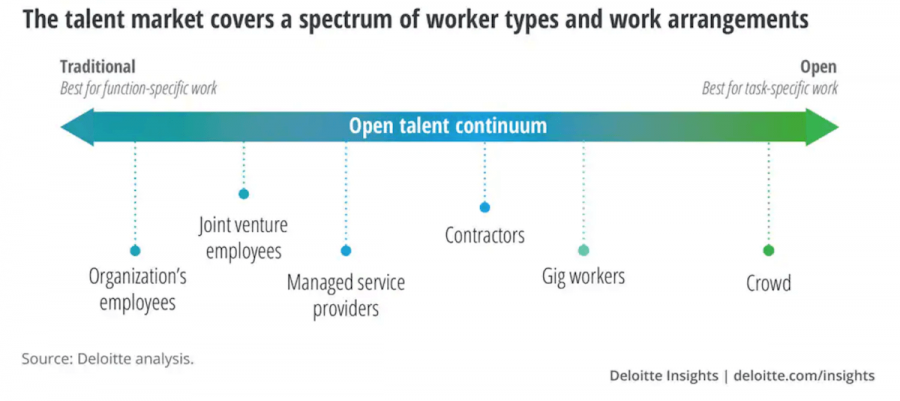
Technology allows organizations to leverage a continuum of full-time employees and freelancers to managed services and gig workers in the most cost-efficient way.
Companies will reconsider the employee lifecycle. They’ll use multiple employment formats to obtain the creativity, passion, experience, expertise, and skill sets needed for the project at hand.
As such, hiring will focus on problem-solving ability and task performance rather than filling roles in the org chart.
Where the Work Is Done
New communication platforms break down barriers among multiple office locations and remote teams to enable seamless collaboration. Organizations can transcend the limitations of distance and tap into a global talent pool so tasks can be completed as cost-effectively as possible.
However, the distributed model isn’t merely a way to increase efficiency or reduce overhead. It also requires companies to rethink how they can foster culture and team connections within a virtual working environment to nurture and retain increasingly scarce talent.
Key Emerging Technologies That Will Reshape the Future Of Work
The notion of work is fast evolving, and here are the key emerging technologies that impact the future of work:
Visual, Low-Code Process Automation
Automation, as distinguished from AI, is foundational to reaping the benefits of upcoming technologies. For example, it produces digital data, which is the fuel for machine learning.
Automation is key to increasing efficiency, reducing human error, and lowering operational costs. Fewer workers will be needed for repetitive tasks, and more employees will focus on strategic decision-making and creative problem-solving.
There are two main types of process automation technologies – Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Business Process Automation (often called Business Process Management or BPM.)
RPA automates individual tasks that are repetitive and time-consuming with very little added value (e.g., faster data entry.) It cuts cost without the need to change the underlying infrastructure. Meanwhile, BPM is the automation of end-to-end business processes (e.g., more accurate decision-making). BPM often serves as the strategic foundation of an organization’s digital transformation.
Automation will prompt businesses that rely on repetitive processes to assess how to improve efficiency. They’ll need to retrain and reallocate workers to take on roles that can utilize their experience and institutional knowledge in a strategic capacity.
Cloud-Based Communication Platforms
Unified communications (UC) platforms enable organizations to leverage the benefits of a remote workforce effectively. These cloud-based technologies help streamline workflow, facilitate collaboration, and increase efficiencies.
They enable real-time communication and collaboration through functionalities such as voice and video calls, instant messaging, screen and file sharing. They allow companies to access a global workforce and attract talent without being hindered by inefficient communications.
A UC platform that offers a reliable environment for effective communication is the “hub” of a digital workplace. It changes how and where work gets done, prompting a re-thinking of “workplace” and introducing a global element to many workforces.
AI-Driven Technologies
The artificial intelligence (AI) umbrella encompasses machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, natural language generation, and more.
The use of AI allows organizations to efficiently extract insights from their proprietary business data for accurate and timely decision-making. Of course, organizations must first embrace automation to generate this business data. For example, automation and analysis of the resulting data can increase the efficiency of an organization’s procurement process by enabling accurate demand forecasting in real-time.
Meanwhile, the reduction of repetitive tasks allows employees to focus on strategic and creative work that’s more valuable and meaningful. AI is making work more enjoyable and fulfilling by augmenting the capabilities of knowledge workers.
AI’s ability to process a large amount of data and extract insights is crucial. It helps humans cut through the clutter and figure out where to focus their attention to enhance strategic thinking and decision-making.
Digital Talent Platforms
The ability to access talent from all over the world through a variety of work arrangements is promoting organizations to reconsider their talent model and employee lifecycle.
The use of digital talent platforms reduces the impact of a mismatch between skills, availability, and location. Companies will shift from filling specific “roles” to hiring talent based on the skills required to complete a specific project successfully.
Digitally-enabled independent workers will be less confined to a specific job title but have to adapt to the objectives of each project to continuously demonstrate value.
With technologies and business requirements always in flux, specific skills will matter less. The ability to obtain new knowledge and adapt to new technological solutions will become the key to success.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing can process data thousands of times faster than traditional silicon-chip-based computers while using less power.
This exponential increase in computing capacity makes it possible to run complex AI-powered applications. They’re used for analytics and modeling, allowing organizations to leverage a large amount of data available.
Quantum computing can support an array of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications. They can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy in training and diagnostic processes.
Also, it can dramatically improve cybersecurity. It’ll reduce IT costs and allow organizations to protect sensitive data effectively when using technologies from cloud-computing platforms to automation software.
Conclusion
When considering the impact of emerging technologies, organizations need to go beyond the bottom line and efficiency.
Take a step back to consider the holistic picture of how the nature of work, the composition of the workforce, and the notion of workplace interact with each other to shape the future of work.
We need both a visionary and pragmatic approach to take full advantage of emerging technologies by imagining the possibilities based on industry-specific data to define a transformational strategy.
Organizations need to rethink workflow, workforce, and workplace from the ground up to take advantage of technologies while creating meaning and value for employees.
Last but not least, companies have to align organizational structure, leadership, and workforce development as they execute a cohesive strategy that goes beyond a short-term equation of cost and efficiency to creating sustainable innovation.